FROSTBITE
Introduction
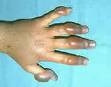
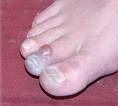
Frostbite is, literally, frozen body tissue - usually skin but sometimes deeper - and must be handled carefully to prevent permanent tissue damage or loss. Children are at greater risk for frostbite than adults, both because they lose heat from their skin more rapidly than adults and because they may be reluctant to leave their winter fun to go inside and warm up. You can help prevent frostbite in cold weather by dressing your child in layers, making sure s/he comes indoors at regular intervals, and watching for frostnip, frostbite's early warning signal.
Frostnip usually affects areas that are exposed to the cold, such as the cheeks, nose, ears, fingers, and toes, leaving them white and numb. Frostnip can be treated at home.
What to Do:
- Bring your child indoors immediately.
- Remove all wet clothing. Wet clothes draw heat from the body.
- Immerse chilled body parts in warm (not hot) water until all sensation returns.
- Don't let your child control the water temperature during rewarming. Numb hands won't feel the heat and can be severely burned by water that is too hot.
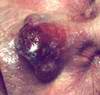
Frostbite is characterized by white, waxy skin that feels numb and hard. It requires immediate emergency medical attention.
What to Do:
- Get your child into dry clothing, then take him/her to a hospital emergency room. If feet are affected, carry them.
- If you cannot get your child to a hospital right away or must wait for an ambulance, give him a warm drink and begin first-aid treatment:
- Immerse frozen areas in warm water (around 100 degrees Fahrenheit) or apply warm compresses for 30 minutes. If warm water is not available, wrap gently in warm blankets.
- Do not use direct heat such as a fire or heating pad.
- Do not thaw the area if it is at risk for refreezing, which may cause severe tissue damage.
- Do not rub frostbitten skin or rub snow on it.
- Rewarming will be accompanied by a burning sensation. Skin may blister and swell and may turn red, blue, or purple. When skin is pink and no longer numb, the area is thawed.
- Apply sterile dressing to the area, placing it between fingers and toes if they are affected. Try not to disturb any blisters.
- Wrap rewarmed areas to prevent refreezing, and have your child keep thawed areas as still as possible.
Disclaimer: This information is not intended be a substitute for professional medical advice. It is provided for educational purposes only. You assume full responsibility for how you choose to use this information.
Updated and reviewed by: Barbara Homeier, MD
Date reviewed: January 2005
Originally reviewed by: Steve Dowshen, MD